Invited Speaker

Prof. Maria Jose Lavorante
Institution of Scientific and Technological Research for Defense, ArgentinaSpeech Title: Efficiency improvements in a water electrolyzer by applying a chemical treatment to its electrodes
Abstract: Hydrogen is an energy carrier that has to be produced by the use of energy from a variety of raw hydrogen-rich materials, including water. Electrolysis allows interconverting electricity into hydrogen and this gives the possibility to use this process for the storage of excess renewable energy. Therefore, the development or improvement of water electrolyzers, is a promising option for a more efficient use of the renewable resources and the production of hydrogen.
In order to evaluate the effect of applying a chemical pickling treatment to the surface of 316L stainless steel electrodes and to study the benefits or detriments of their performance in alkaline electrolysis of water, four experiments were carried out. Therefore, the following were evaluated: a) a pair of electrodes in their original state (OS); b) one pair after the application of a chemical pickling treatment (ICPT) c) one pair after the application of two treatments (IICPT) and d) one pair after the application of three treatments (IIICPT). The results show that the experiment where both electrodes are subjected to a single chemical pickling treatment present the best performance. Successive treatments lead to a detriment of the efficiency of the pair of electrodes. Figure 1.a, presents the polarization curves of the different experiments at a temperature of 35ºC and 1.b, compares the results obtained from the three systems with chemical pickling treatment at a working temperature of 52ºC. At applied potential differences close to the decomposition of water, the values of current density do not seem to be significant. Current density of ICPT becomes more noticeable, on average, 54% higher when compared with IICPT and 167% higher when compared with IIICPT.
Then, the inorganic ions present were identified in the solution resulting from the chemical pickling treatment. The process was carried out in a systematic way, using recognition chemical reactions, through the formation of complexes or salts that are evidenced by unique and characteristic colors. The cations analyzed were nickel, chromic, ferrous and ferric. The cation present in the solution is ferrous. Throughout the speech there will be a detailed description of the treatments used and the chemical analysis performed.
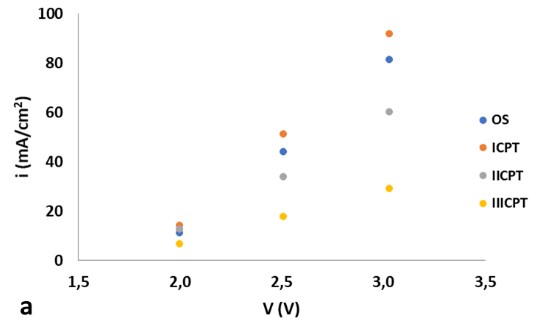
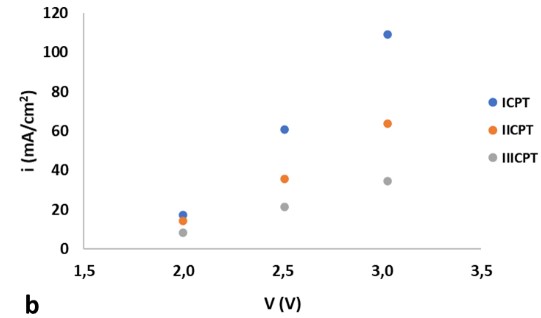
Figure 1. Polarization curves: a) of the four experiments at 35ºC and b), results obtained from the three systems with chemical pickling treatment at 52ºC.
